Pulse In Action
Possible physiology engine applications

Virtual/Augmented Environments

Cyber-Physical Simulations
Digital Twin Modeling
Synthetic Data Generation

In Silico Investigations
Multiscale/Multiphysics Pipelines
There is a wide range of potential applications, a few include:
- Powering serious games for medical education and training
- Producing responsive physiology in real time for manikin training
- Performing in silico experiments to reduce the need for expensive lab work and clinical trials
- Integrating a single-system model into the engine to understand full-body physiologic response
- Providing synthetic patient inputs and outputs for sensor systems
- Providing synthetic data for Machine Learning algorithm development
- Enabling hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulated patients testing solutions
- Teaching and education interactive content
- Supporting rapid prototyping of medical devices, algorithms, and treatment strategies with a high-fidelity virtual patient model
- Pairing with virtual surgery planning/rehearsal
- Creating digital twins based on real clinical data
- Simulating multiscale modeling approaches with mixed fidelity
- Integrating with multiphysics pipelines
Featured Applications and Investigations
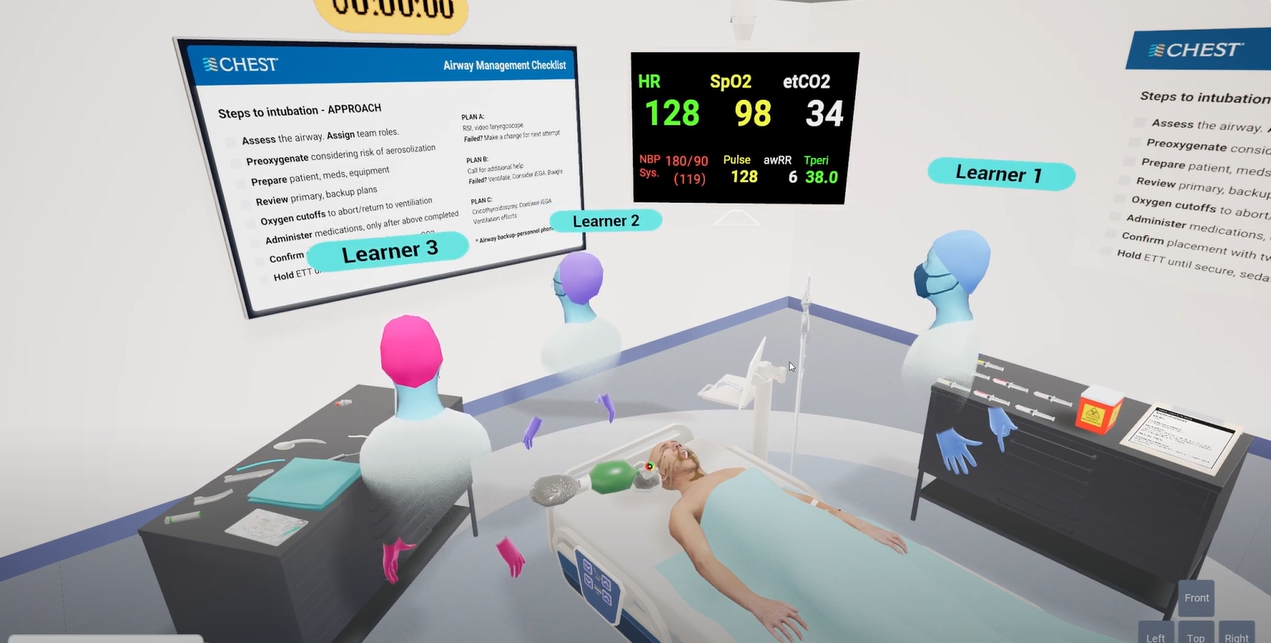
To feature your Pulse use case, please email us at kitware@kitware.com!VRescue - The VR training simulation for emergency medicine
VRescue allows trainees in the rescue service to gain significantly more practical experience without requiring additional teaching staff. This solution complements traditional practical training in a meaningful way by creating additional exercise opportunities without any additional burden on personnel or organization. Pulse is of particular importance for emergency medical training simulations like VRescue. Integration of Pulse into VRescue provides a realistic representation of examination and treatment options required for plausible, flexible, and reliable data on the medical condition of patients
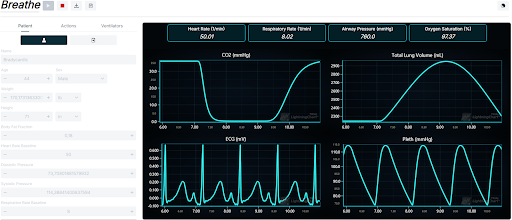
BREATHE - A Respiratory System Simulator for Mechanical Ventilator Testing and Training
An application designed to train healthcare professionals in the use of mechanical ventilators and to test external ventilators. It allows users to simulate a realistic environment where they can configure patients with various medical conditions and apply ventilators in modes. Users can adjust ventilator parameters to optimize patient care and acquire practical skills. Additionally, BREATHE is able to real-time data exchange between the simulation and external devices. External ventilators can receive simulated patient data and send their own feedback (e.g. pressure and volume), allowing users to verify their performance and calibration. Moreover, middleware can be connected to log simulation data, supporting detailed analysis and future review.
In the Moment
DARPA In the Moment (ITM) program explores how AI can reliably support human decision-makers in complex, high-stakes environments.
The program’s broader mission is to create AI systems that not only make accurate recommendations but also reflect human reasoning, values, and priorities.
Kitware focused on military medical triage in resource-constrained settings, where speed, accuracy, and trust are paramount.
Realistic testing was achieved using Pulse to generate synthetic patient profiles across a broad spectrum of medical scenarios.
To ensure that the AI could reflect diverse human decision-making, the system incorporated few-shot learning and domain adaptation, enabling it to adapt dynamically to individual decision styles.
AI-Driven Medical Triage Assistance
Leveraging Pulse to develop advanced AI algorithms for medical triage. By integrating physiological simulations with AI the research aims to enhance decision-making during triage improving the identification of patients needing life-saving interventions. The approach combines real-time physiological data with machine learning to support healthcare professionals in high-stress environments offering a reliable tool to prioritize patient care and improve outcomes.
Optimal Control for Mechanical Ventilation
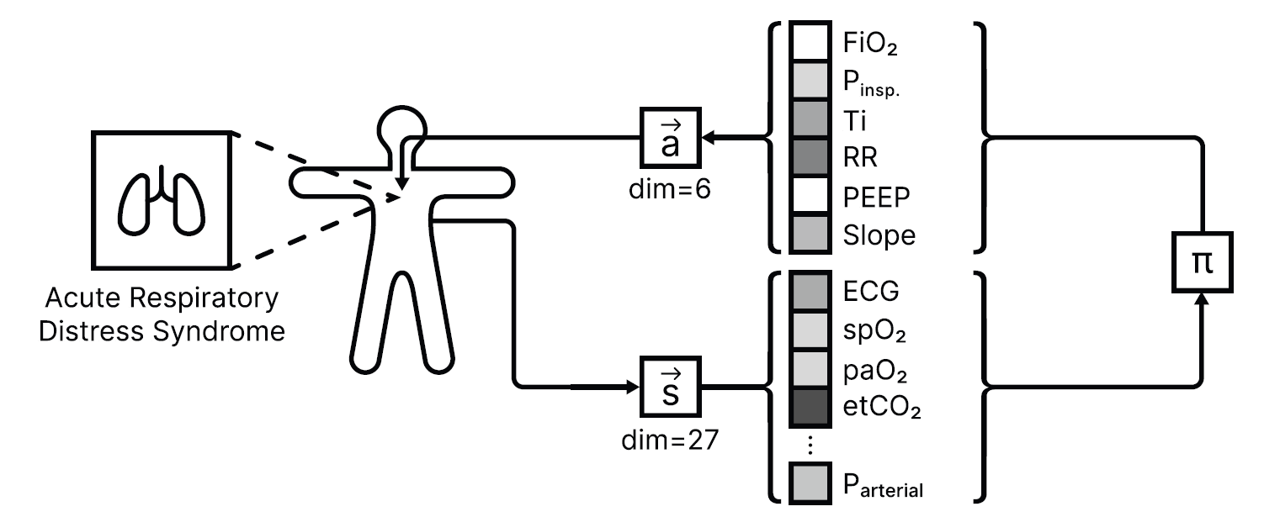
Pulse was leveraged to develop an optimal control framework for mechanical ventilators specifically targeting patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). By integrating machine learning techniques including neural networks the project demonstrated the ability to automatically discover effective ventilation strategies without relying on traditional clinical guidelines. This approach was validated against established protocols like ARDSnet showing promising results in improving patient outcomes through real-time adaptive ventilation management.
Collaborative VR for Advanced Liver Surgery Training
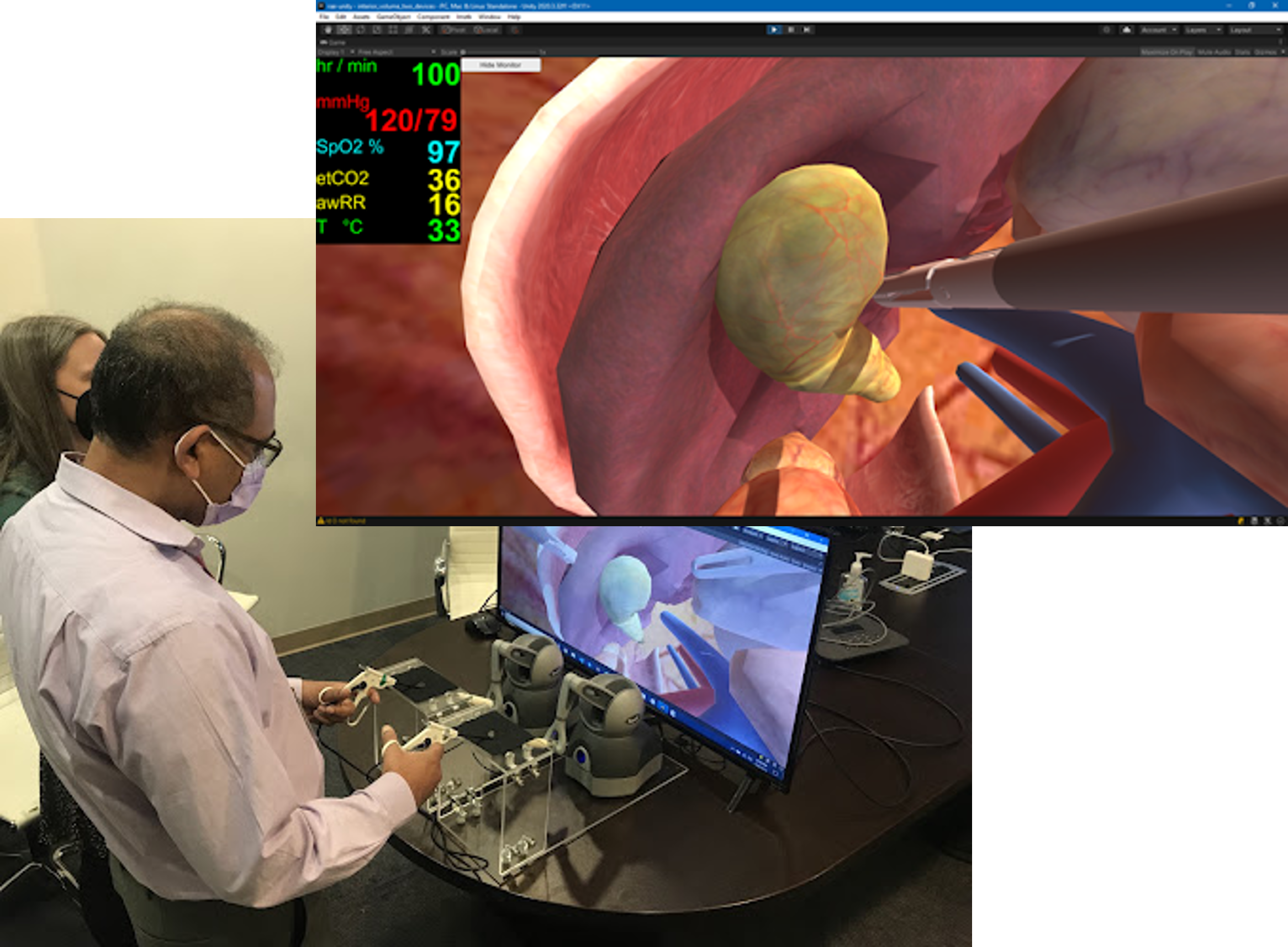
Pulse was integrated into a collaborative virtual reality (VR) environment designed to enhance liver surgery training and planning. This VR environment provides a comprehensive simulation experience allowing multiple users to engage in surgical planning resection simulations and laparoscopic training. By incorporating real patient data and realistic physiological responses the system offers an immersive and effective platform for surgical education. The integration of Pulse ensures that the simulated physiological feedback is both accurate and responsive supporting the development of critical skills in a controlled and interactive setting.
Primary Blast Lung Injury Multiphysics Simulation
A versatile cloud-based multiphysics simulation software used to characterize the physiological response of human lungs due to underwater explosions (UNDEX). The outcome of patients subjected to primary blast lung injury (PBLI) is strongly dependent on the severity and location of lung damage. Therefore, the Pulse cariopulmonary model further discritized to allow for the implementation of heterogenous lung damage. The tool has the potential to improve risk modeling for establishing safe standoff distances for Explosive Ordnance Disposal divers working around explosives.
Virtual Reality for Advanced Clinical Skills Training
Pulse has been integrated into a large-scale virtual reality (VR) platform designed to enhance clinical skills training, with a specific focus on brain death diagnostics. This VR environment provides healthcare professionals with a dynamic and immersive training experience, allowing them to practice and refine their skills in brain death examination. The use of Pulse ensures that the physiological feedback is both accurate and responsive, creating realistic scenarios that prepare trainees for critical decision-making in real-world clinical settings.
Assessment of Digital Twin Accuracy
This work leverages Pulse as the key case study for its digital twin assessment methodology. By applying its rigorous statistical falsification method, the work analysed the engine's ability to replicate real-world outcomes for critically ill sepsis patients using data from the MIMIC-III ICU dataset. The analysis revealed specific discrepancies, offering valuable feedback for refining the model's accuracy in predicting physiological responses. These findings contribute to the ongoing improvement of the Pulse engine, ensuring more reliable simulations for use in critical care research and decision-making.
Surgical Simulator Coupling
A medical training simulator designed to manage rare and adverse events has been developed by integrating the Pulse Physiology Engine with the Interactive Medical Simulation Toolkit (iMSTK). The trainer allows healthcare professionals to practice complex scenarios with real-time physiological feedback. The system includes detailed models that respond autonomously to medical interventions, enhancing the realism and effectiveness of training in critical care environments.
VR Medical Training
A Pulse plugin for Unreal Engine enhancing VR-based medical training simulations. This collaboration allows for real-time patient feedback within immersive environments, enabling healthcare professionals to practice and refine their skills in highly realistic scenarios. The integration ensures that patient responses are accurately modeled and autonomously driven, providing a dynamic and interactive training experience that improves the preparedness and confidence of medical teams.
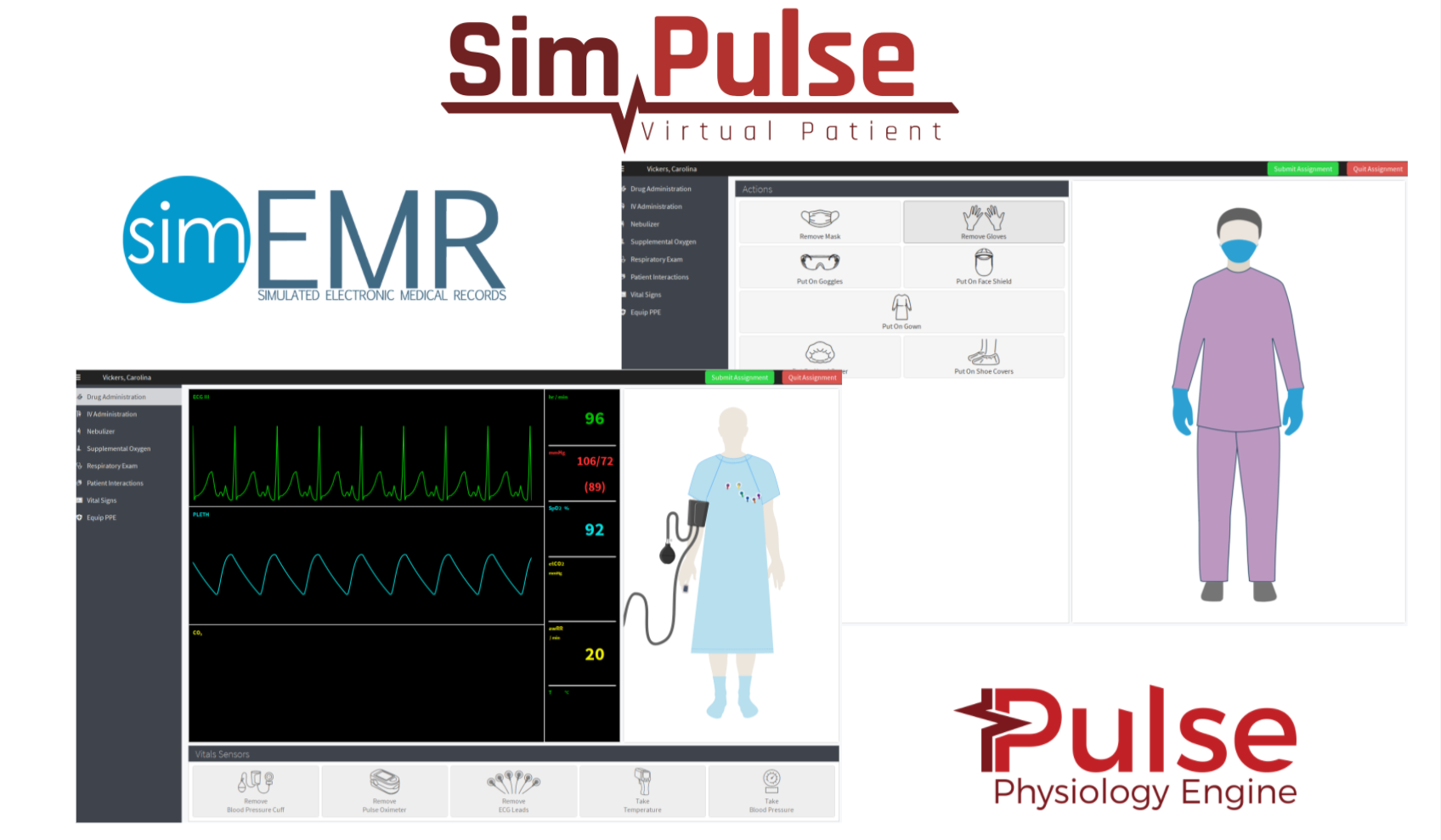
SimPulse
SimPulse utilizes Kitware’s Pulse Physiology Engine (“Pulse”) and integrates with SimEMR, KbPort’s Simulated Electronic Medical Record Platform (“SimEMR”). SimPulse combines the well-established training modules in SimEMR and the accurate physiological patient feedback produced by the Pulse engine in a simple, intuitive user-interface, to provide an accurate context of patient care by presenting healthcare learners with real-time, physiological and pharmacological patient data required for clinical decision-making and documentation. Well-suited for use in lab, classroom, and remote settings, SimPulse supports critical learning elements such as patient safety, medication administration, patient interactions, and patient vitals.
Computational Life
Computational Life provides personalized patient outcome predictions using computational models. Kitware and Computational Life have worked together to create a multi-fidelity, multi-scale model. This model couples a whole body lumped-parameter model with a one-dimensional computational fluid dynamics cardiovascular model to capture pressure and flow wave propagations throughout the body. The goal is to advance patient-specific predictions.
NP Skills Labs
The Clinic Immersives NP Skills Labs Enterprise allows nurse practitioner (NP) students to develop clinical lab skills using their own affordable Oculus Quest mobile VR. With this tool, students have unlimited access to perform virtual procedures anywhere at any time. This product also features hand tracking inputs that allow students to practice in either guided or expert modes.
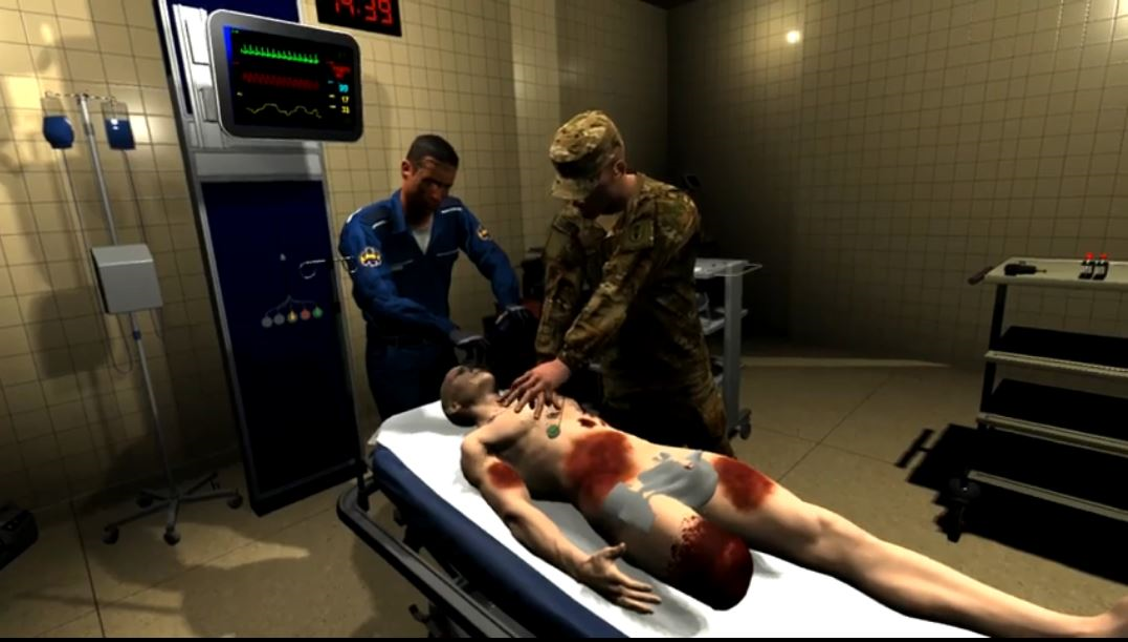
Trauma Simulator
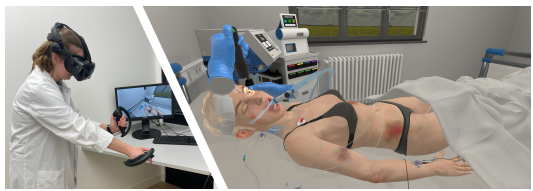
An immersive virtual reality emergency medicine training simulator for military medical personnel. This simulator uses the Unity game engine and Pulse to provide dynamic physiological feedback on the patient's condition from a wide range of injuries and treatments.
COVID-19 Multipatient Ventilation
An in silico investigation to help critical care physicians predict the risks associated with connecting multiple patients to a shared ventilator.
Distance Learning and Online Education
A partnership to demonstrate how the Pulse Physiology Suite can enhance the use of SimEMR to train medical professionals. Distance learning and online education have become a significant source of education during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Ventilation Management Trainer
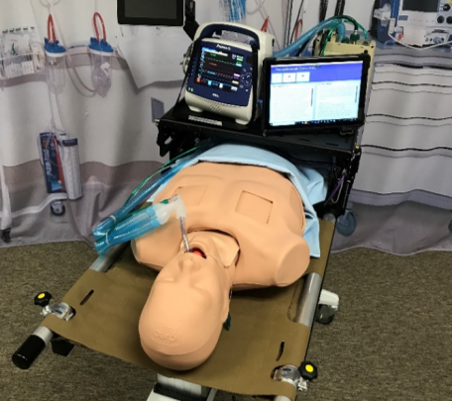
A training simulator designed to mimic respiratory distress during mechanical ventilation. A simulated torso was developed and integrated with a Special Medical Emergency Evacuation Device. It is affixed with medical equipment utilized during Critical Care Air Transport Team missions. The torso includes a lung model, upper airway, and head with reproducible computerized algorithms. The simulator is responsive to treatment of conditions encountered during mechanical ventilation.
Pulse is fully integrated to autonomously drive all patient responses.
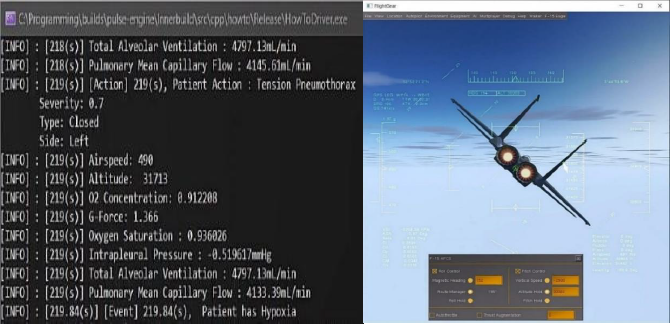
Flight Simulator Coupling
A coupled FlightGear flight simulator and Pulse physiology engine to recreate and understand hypoxic events, related to a combination of high FiO2 and high g-forces. Global data is shared between the FlightGear and Pulse by creating interdependency between the two applications known as coupling. By coupling interactive simulations based on FlightGear and Pulse, hypoxic events were recreated from two scenarios: simulated acceleration atelectasis, achieved by using high g-forces output from FlightGear with a modified Pulse tension pneumothorax scenario, and the combination of high g-forces and high FiO2, based on a prototype OBOGS simulation.
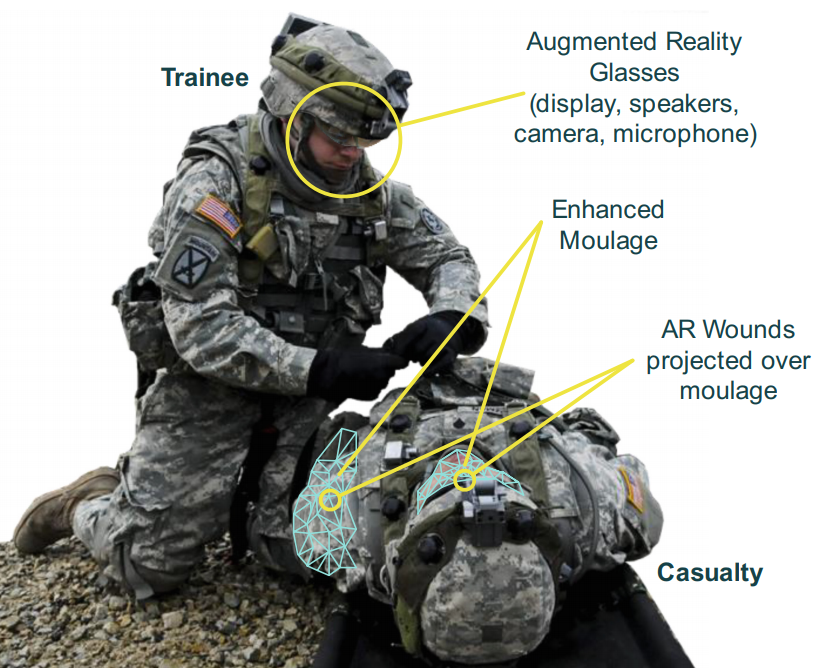
Combat Casualty Care Augmented Reality Intelligent Training System (C3ARESYS)
An augmented reality system to improve the realism of Combat Medics (68W) and Combat Lifesavers scenario-based training. C3ARESYS provides the opportunity to train on wounds and casualties that respond to treatments with feedback adapted to the trainee's skill level. C3ARESYS offloads work from the instructor, enabling focus on teaching rather than fixing shortcomings in casualty simulation.
Pulse is used to provide dynamic interactions to the patient and provide physiological feedback from the patient.
Closed-Loop Physiology Management System
A system for investigating closed-loop physiology management for critical care with in-silico patients. Closed-Loop Assistants (CLAs) are designed to leverage medical device interfaces to add computers/algorithms to the clinical care loop to aid indecision-making and to implement the automatic application of interventions.
Links
- Blog Post
- CLASim Website
- CLASim Repository
- "Towards A Test and Validation Framework for Closed-Loop Physiology Management Systems for Critical and Perioperative Care"
- "Simulation-Based Test and Validation of Medical Cyber-Physical Systems for Critical and Perioperative Care"
- "A Proof-of-Concept Framework for Testing and Validating Networked Medical Device Applications and Closed-Loop Physiology Management Systems for Critical and Perioperative Care"
- "Testing and Validation Framework for Closed-Loop Physiology Management Systems for Critical and Perioperative Care"
The BioMojo Virtual Patient Experience (VPE)
An interactive, multiplayer 3D healthcare and medicine themed, STEM education product. BioMojo VPE is designed to inspire and educate youth towards careers in healthcare, clinical research and biomedical engineering through fun, challenging virtual role play, teamwork, and problem-solving. Themes include emergency medicine, preventable chronic diseases, physiology, anatomy, genomics, and pharmacotherapy.
Players will perform (virtual) diagnostic procedures and other interactions with virtual patient avatars. Virtual patient physiology is provided by Pulse.
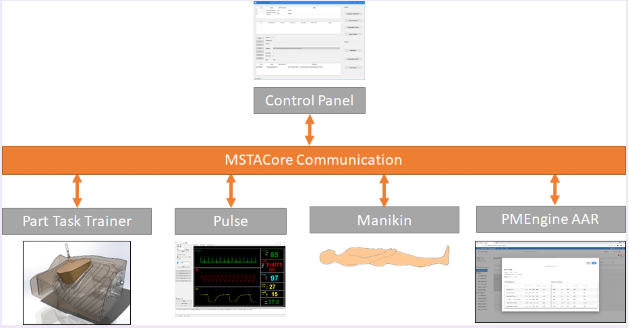
Medical Simulation and Training Architecture (MSTA)
The MSTA platform provides an open standard to connect manikins, part-tasks trainers, physiology engines, and other simulation technologies to support the creation of complex training systems necessary for future force readiness efforts.
MSTA successfully demonstrated an integrated TCCC training scenario that took a wounded virtual patient from field care to role 2 care. The training system consisted of a manikin, a custom control panel, a part task trainer, the Pulse physiology engine and an after action review engine.
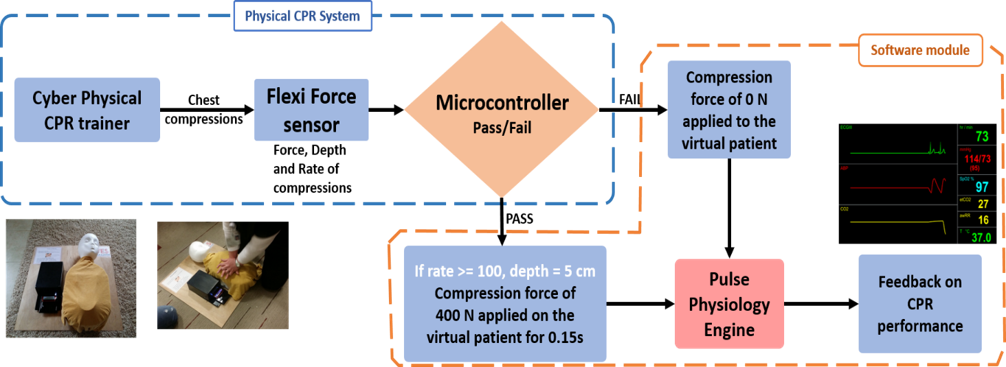
CPR Training System
A CPR simulator with real-time compression feedback and features to monitor performance metrics, such as time-to-CPR, compression depth, and rate. This system is controlled by a microcontroller to count the number of chest compressions and ghe pressure applied. The data is passed to the Pulse physiology engine in real-time and the state of the patient changes dynamically based on sensor inputs.
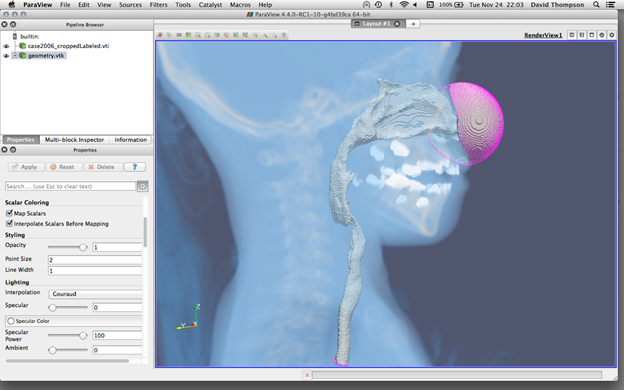
Virtual Pediatric Airway Workbench (VPAW)
A surgical planning tool for subglottic stenosis that incorporates three major components.
VPAW initiates with a CT scan of the patient and obtains a geometrical model through segmentation and surface reconstruction.
It then employs a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) engine based on a Lattice-Boltzmann formulation to provide airflow parameters for Pulse. Pulse then provides the physiologic response due to the airflow.
A real-time geometric authoring tool allows surgeons to edit the tracheal geometry using a haptic device as part of a surgical planning. VPAW calculates the physiologic results of each plan to be assessed by surgeons to identify the best course of action.
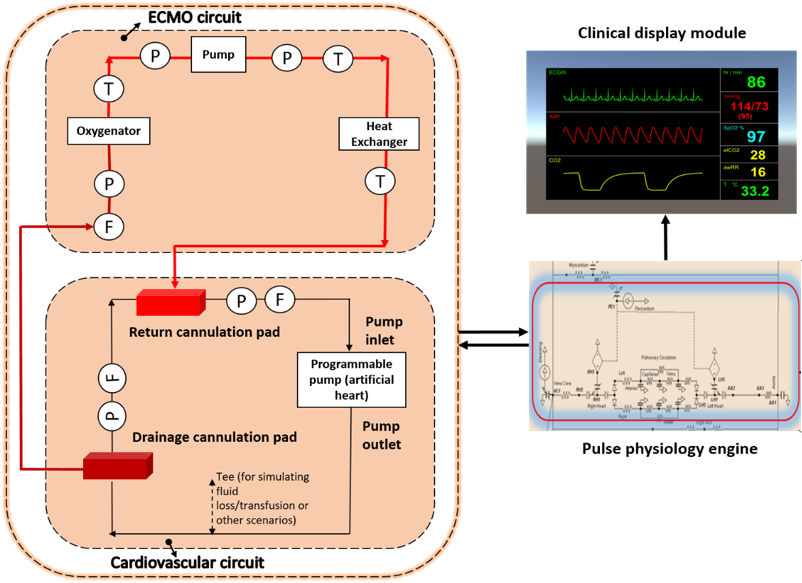
Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Training Simulator
A full-fledged training simulator of various procedures and scenarios involved in ECMO and the associated complications. The simulator has three main parts:
- A physical cardiovascular circuit that mimics the human circulation system, including an artificial human heart and a synthetic vasculature with cannulation pads.
- A physical ECMO circuit to simulate oxygenation with a color changing blood simulant, an external pump to regulate flow, and sensors to monitor vitals.
- A mathematical model of human physiology simulating respiratory failure and cardiac arrest based on Pulse Physiology Engine. Pulse helps to simulate clinical scenarios (i.e., hypovolemia, hypoxia, etc.) by controlling the cardiovascular and ECMO circuits, and provides real-time physiological feedback for experimental training.
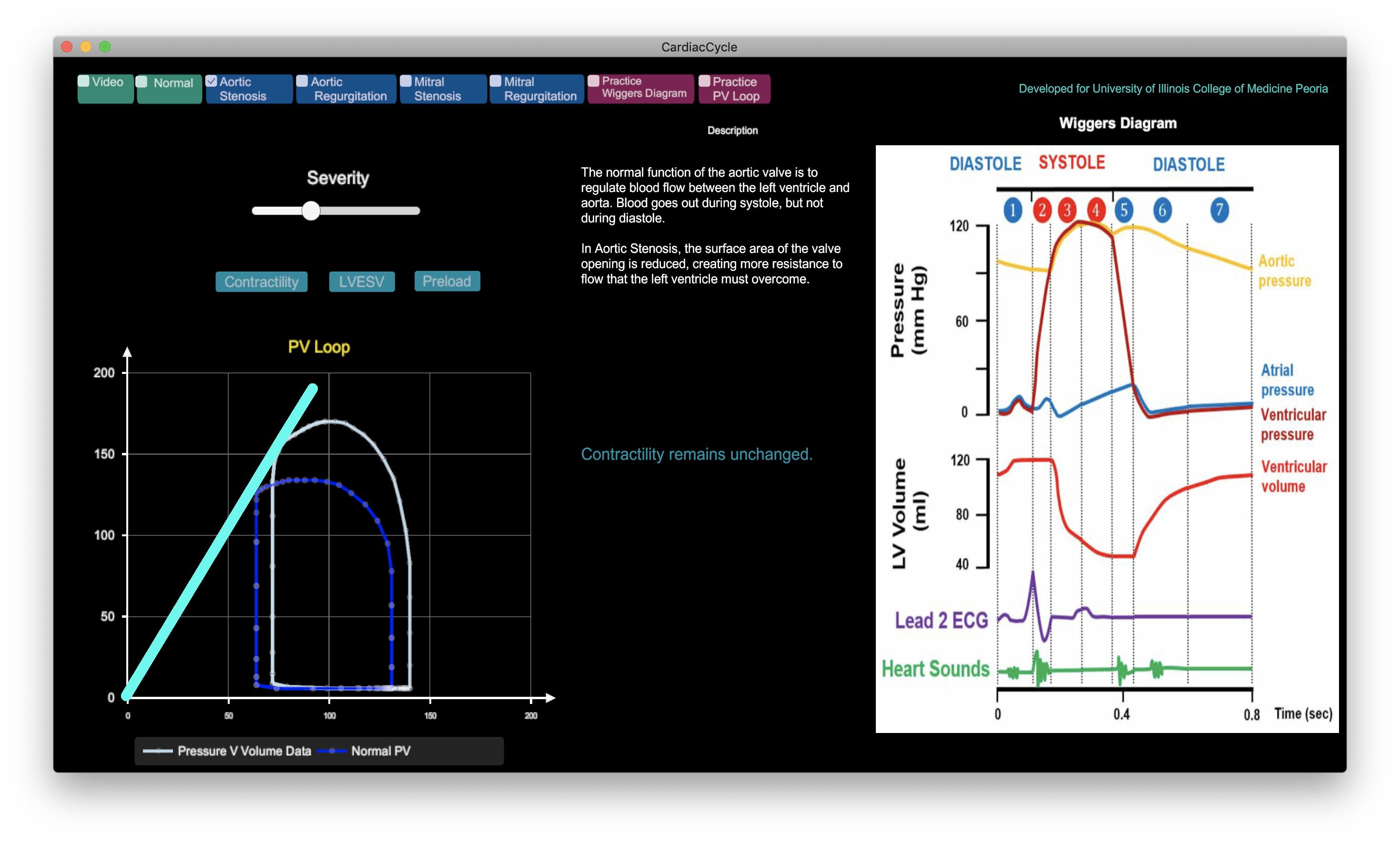
Modeling Valvular Diseases
Simulating three valvular conditions: aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, and mitral stenosis. Pulse virtual physiology software has the potential to transform medical education by allowing medical students to learn in a consequence-free environment. Medically accurate physiology models are required to ensure that lessons learned virtually translate to the real world.
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Performance
A high-fidelity computational surrogate head model focused on the ventricular system to optimize the performance of ventriculoperitoneal shunts. The cerebrospinal fluid model is being coupled with the cerebrovascular system using the Pulse physiology engine. In addition to globally quantifying the essential cerebrovascular parameters for the local high-fidelity analysis of shunt function, Pulse also provides an invaluable training capability to teach students about the effects of elevated ICP due to hydro-cephalus on the entire body.

SOFA Integration
Created an interface plugin within the SOFA multi-physics simulation framework to link with the Pulse physiology engine.
Modular Deployment
Pulse is deployable on low size, weight, power, and cost (SWaP-C) systems, and has been shown to run faster than real-time on several single-board computers.
Distributed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
See accompanying NOTICE file for details.
Generated 2026-02-01 - 10710baa2